|
Size: 5867
Comment:
|
Size: 6237
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| ["Main"] + ["What Is Subversion For"] .+ ["Setting Up A Subversion Repository"] .+ ["SVNKit Architecture"] |
[[Main]] + [[What_Is_Subversion_For|What Is Subversion For]] .+ [[Setting_Up_A_Subversion_Repository|Setting Up A Subversion Repository]] .+ [[SVNKit_Architecture|SVNKit Architecture]] |
| Line 6: | Line 6: |
| .+ ["Authentication"] .+ ["Managing Repository With SVNKit"] .+ ["Printing Out A Subversion Repository Tree"] .+ ["Printing Out File Contents"] .+ ["Printing Out Repository History"] .+ [:Committing To A Repository:Editing operation: committing to a repository] .+ [:Updating From A Repository:Editing Operation: receiving changes from a repository] .+ ["Replicating An Existing Repository"] .+ ["Managing A Working Copy"] |
.+ [[Authentication]] .+ [[Managing_Repository_With_SVNKitManaging_Repository_With_SVNKit|Managing Repository With SVNKitManaging Repository With SVNKit]] .+ [[Printing_Out_A_Subversion_Repository_Tree|Printing Out A Subversion Repository Tree]] .+ [[Printing_Out_File_Contents|Printing Out File Contents]] .+ [[Printing_Out_Repository_History|Printing Out Repository History]] .+ [[Committing_To_A_Repository|Editing operation: committing to a repository]] .+ [[Updating_From_A_Repository|Editing Operation: receiving changes from a repository]] .+ [[Replicating_An_Existing_Repository|Replicating An Existing Repository]] .+ [[Managing_A_Working_Copy|Managing A Working Copy]] |
| Line 18: | Line 18: |
| [[TableOfContents]] | <<TableOfContents>> |
| Line 21: | Line 21: |
| When you have downloaded [http://svnkit.com/download/index.php the latest SVNKit binaries] and ready to start using it, a question arises: what initialization steps should be performed in order to set up the library? Direct interacting with a ["Subversion"] repository is carried out by a low-level layer, where the main class representing a repository access driver interface is an abstract [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html SVNRepository] class. There are several protocol specific realizations of this driver, one for each protocol. Each driver is created by an abstract factory class - [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html SVNRepositoryFactory], which also has several protocol specific realizations, each one for each protocol. The following table matches a protocol against a corresponding [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html SVNRepositoryFactory] realization: | When you have downloaded [[http://svnkit.com/download/index.php|the latest SVNKit binaries]] and ready to start using it, a question arises: what initialization steps should be performed in order to set up the library? Direct interacting with a [[Subversion]] repository is carried out by a low-level layer, where the main class representing a repository access driver interface is an abstract [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html|SVNRepository]] class. There are several protocol specific realizations of this driver, one for each protocol. Each driver is created by an abstract factory class - [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html|SVNRepositoryFactory]], which also has several protocol specific realizations, each one for each protocol. The following table matches a protocol against a corresponding [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html|SVNRepositoryFactory]] realization: |
| Line 30: | Line 30: |
| /!\ Prior to using the library you must set up an appropriate [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html SVNRepositoryFactory] realization for a particular protocol. For example, if you would like to work with a repository via the {{{svn://}}} protocol, you must register the following factory: | /!\ Prior to using the library you must set up an appropriate [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html|SVNRepositoryFactory]] realization for a particular protocol. For example, if you would like to work with a repository via the {{{svn://}}} protocol, you must register the following factory: |
| Line 41: | Line 41: |
| After this step [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html SVNRepositoryFactory] knows how to create [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html SVNRepository] drivers specific for the {{{svn://}}} protocol since it now contains the registered factory. And further you create a driver itself: | After this step [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html|SVNRepositoryFactory]] knows how to create [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html|SVNRepository]] drivers specific for the {{{svn://}}} protocol since it now contains the registered factory. And further you create a driver itself: |
| Line 54: | Line 54: |
| In ["SVNKit"] all repository urls are represented by the [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/SVNURL.html SVNURL] class. If a path string is not ''UTF-8'' encoded yet, use the [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/SVNURL.html SVNURL]'s [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/SVNURL.html#parseURIDecoded(java.lang.String) parseURIDecoded()] method to create a new url representation (it will be encoded if necessary). Then you pass the url representation to the [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html SVNRepositoryFactory] to create a new [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html SVNRepository] driver. So, this way you can bind your driver to any repository location you would like. | In [[SVNKit]] all repository urls are represented by the [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/SVNURL.html|SVNURL]] class. If a path string is not ''UTF-8'' encoded yet, use the [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/SVNURL.html|SVNURL]]'s [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/SVNURL.html#parseURIDecoded(java.lang.String)|parseURIDecoded()]] method to create a new url representation (it will be encoded if necessary). Then you pass the url representation to the [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepositoryFactory.html|SVNRepositoryFactory]] to create a new [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html|SVNRepository]] driver. So, this way you can bind your driver to any repository location you would like. |
| Line 56: | Line 56: |
| attachment:SVNRepository_connection2.png | {{attachment:SVNRepository_connection2.png}} |
| Line 58: | Line 58: |
| The diagram above illustrates how different drivers are created for different repository paths: one for the repository root ({{{svn://host/path_to_root}}}), one for a directory ({{{svn://host/path_to_root/dirA}}}) and one for a file ({{{svn://host/path_to_root/dirB/fileB1}}}). Most operations which [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html SVNRepository] driver can perform against a repository, accept a repository path which may be one of two types: | The diagram above illustrates how different drivers are created for different repository paths: one for the repository root ({{{svn://host/path_to_root}}}), one for a directory ({{{svn://host/path_to_root/dirA}}}) and one for a file ({{{svn://host/path_to_root/dirB/fileB1}}}). Most operations which [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html|SVNRepository]] driver can perform against a repository, accept a repository path which may be one of two types: |
| Line 67: | Line 67: |
| When you use SVNKit for managing Working Copies you also should set up appropriate factory classes since the high-level layer uses the low-level one for working with a repository. If you miss this initialization step you may get an exception saying that ["SVNKit"] could not create an [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html SVNRepository] object for the provided url. | When you use SVNKit for managing Working Copies you also should set up appropriate factory classes since the high-level layer uses the low-level one for working with a repository. If you miss this initialization step you may get an exception saying that [[SVNKit]] could not create an [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/io/SVNRepository.html|SVNRepository]] object for the provided url. |
| Line 71: | Line 71: |
| All high-level operations for managing Working Copies are logically divided to ["SVN*Client"] classes: each ["SVN*Client"] class joins a separate group of operations (for example, [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/wc/SVNUpdateClient.html SVNUpdateClient] provides API on update operations, such as checkout, update, switch, export). There're two different ways of instantiating objects of these classes: | All high-level operations for managing Working Copies are logically divided to [[SVN*Client]] classes: each [[SVN*Client]] class joins a separate group of operations (for example, [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/wc/SVNUpdateClient.html|SVNUpdateClient]] provides API on update operations, such as checkout, update, switch, export). There're two different ways of instantiating objects of these classes: |
| Line 73: | Line 73: |
| * Create only necessary ["SVN*Client"] objects. * Create a single [http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/wc/SVNClientManager.html SVNClientManager] instance which provides objects of necessary ["SVN*Client"] types. |
* Create only necessary [[SVN*Client]] objects. * Create a single [[http://svnkit.com/kb/javadoc/org/tmatesoft/svn/core/wc/SVNClientManager.html|SVNClientManager]] instance which provides objects of necessary [[SVN*Client]] types. |
- - Getting Started With SVNKit
+ Managing Repository With SVNKitManaging Repository With SVNKit
Contents
How to use different repository access protocols in SVNKit?
When you have downloaded the latest SVNKit binaries and ready to start using it, a question arises: what initialization steps should be performed in order to set up the library? Direct interacting with a Subversion repository is carried out by a low-level layer, where the main class representing a repository access driver interface is an abstract SVNRepository class. There are several protocol specific realizations of this driver, one for each protocol. Each driver is created by an abstract factory class - SVNRepositoryFactory, which also has several protocol specific realizations, each one for each protocol. The following table matches a protocol against a corresponding SVNRepositoryFactory realization:
protocol |
SVNRepositoryFactory realization |
svn:// |
SVNRepositoryFactoryImpl |
http:// |
DAVRepositoryFactory |
file:/// |
FSRepositoryFactory |
Instructions on initializing SVNKit
![]() Prior to using the library you must set up an appropriate SVNRepositoryFactory realization for a particular protocol. For example, if you would like to work with a repository via the svn:// protocol, you must register the following factory:
Prior to using the library you must set up an appropriate SVNRepositoryFactory realization for a particular protocol. For example, if you would like to work with a repository via the svn:// protocol, you must register the following factory:
After this step SVNRepositoryFactory knows how to create SVNRepository drivers specific for the svn:// protocol since it now contains the registered factory. And further you create a driver itself:
In SVNKit all repository urls are represented by the SVNURL class. If a path string is not UTF-8 encoded yet, use the SVNURL's parseURIDecoded() method to create a new url representation (it will be encoded if necessary). Then you pass the url representation to the SVNRepositoryFactory to create a new SVNRepository driver. So, this way you can bind your driver to any repository location you would like.
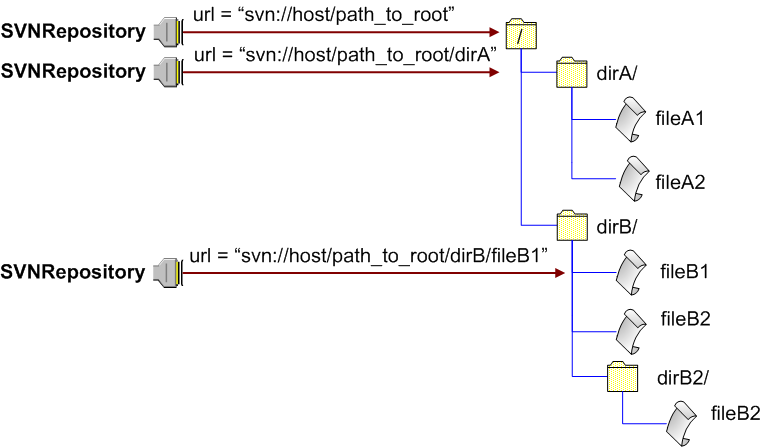
The diagram above illustrates how different drivers are created for different repository paths: one for the repository root (svn://host/path_to_root), one for a directory (svn://host/path_to_root/dirA) and one for a file (svn://host/path_to_root/dirB/fileB1). Most operations which SVNRepository driver can perform against a repository, accept a repository path which may be one of two types:
path that does not start with '/' - is always relative to the location the driver is bound to
path that does start with '/' - is always absolute to the repository root (always starts at the top of the repository tree)
Using high-level layer
When you use SVNKit for managing Working Copies you also should set up appropriate factory classes since the high-level layer uses the low-level one for working with a repository. If you miss this initialization step you may get an exception saying that SVNKit could not create an SVNRepository object for the provided url.
SVN*Client classes
All high-level operations for managing Working Copies are logically divided to SVN*Client classes: each SVN*Client class joins a separate group of operations (for example, SVNUpdateClient provides API on update operations, such as checkout, update, switch, export). There're two different ways of instantiating objects of these classes:
Create only necessary SVN*Client objects.
Create a single SVNClientManager instance which provides objects of necessary SVN*Client types.
